The precise structure and properties of humus substances are highly dependent on the source from which they are isolated and the methods of extraction.
Humic substances are the most common organic macromolecules in nature and have a high carbon content. They are an important component in the soil; they have an effect on the physical and chemical properties of the soil and they improve soil fertility, but also increase the disease resistance of plants/crops so that they can better withstand stress. Humus improves the structure and processability of the soil and increases its moisture retention capacity. Humus also stimulates soil life and increases soil resilience. In nature, humus is replenished faster than it disappears, giving you a build-up of humus and a continuous improvement of the quality of the soil, and yet modern agriculture means that more and more humic acid disappears from our soil every year, impoverishing our agricultural land and decreasing crop yields.
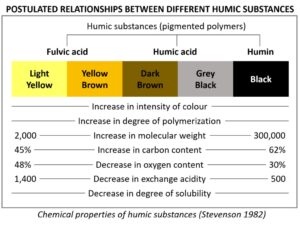
Humic substances
“Humic substances” is a collective term for the following 3 substances:
Humic acid
Characteristics:
Humic acid is characterized by the following qualities:
Fulvic acid
Characteristics:
Fulvic acid is characterized by the following qualities:
Humin
Characteristics:
Humin is characterized by the following aspect:
Effects:
Humic acid is characterized by the following positive effects:
Effects:
Fulvic acid is characterized by the following positive effects:
Effects:
Humin is characterized by the following positive effects: